External users: registration to be carried out only through I-STEM portal
Additional information about sample and analysis details should be filled in the pdf form provided in the I-STEM portal under “DOWNLOAD CSRF”
Internal users (IITB): registration to be carried out only through DRONA portal
Additional information about sample and analysis details should be filled in the pdf form provided here.
.
Category
- Material Characterization » Mechanical Characterisation
Booking Details
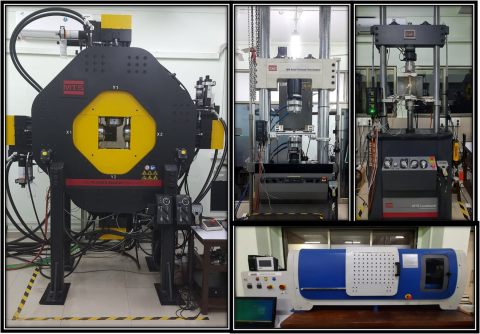
Facility Management Team and Location
Facility Features, Working Principle and Specifications
Features :
1. Planar Biaxial System – 100kN:
This system employs multiaxial loading technology to apply and measure in-plane stresses in both the X and Y axes
a) Strain measurement
Using DIC and Video extensometer
High Temperature Test Facility Upto 600oC
2. Axial Torsion Test System-250kN/2000Nm:
a) Video extensometer:
This is an Optical (non-contact) instrument to measure strain on specimen.
b) Electronic extensometer
Room Temperature:
Fixed gauge length: 25 mm (max. elongation 50% of gauge length)
Variable gauge length: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 mm
5 mm and 10 mm dynamic extensometer
High Temperature (up to 14000C ):
Gauge length: 12mm (Max. elongation +20%/-10%)
Multi-axial Extensometer:
Gauge length: 25 mm
c) Clip on gauge or CTOD gauge
Gauge length: 5 and 12 mm
d) Environmental chamber
Temperature Range: -120 0C to +350 0C
e) Furnaces
Two zone furnace: 200-1200 degC ( Min. Gauge Length: 120 mm)
Three zone furnace: 200-1200 degC (Min. Gauge length: 16 mm) **Threaded samples are required.
f) Three Point and Four Point bend fixtures
Span: 38-305 mm
3. Axial Fatigue System- 100kN:
a) Video extensometer
This is an Optical (non-contact) instrument to measure strain on specimen.
b) Electronic extensometer
Room Temperature:
Fixed gauge length: 25mm (max. elongation 50% of gauge length)
Variable gauge length: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 mm
5 mm and 10 mm dynamic extensometer
High Temperature (up to 1200 degC ):Gauge length: 12mm (Max. elongation +20%/-10%)
c) Clip on gauge or CTOD gauge
Gauge length: 5 and 12 mm
d) Environmental chamber
Temperature Range: -120 0C to +350 0C
e) Furnaces:
Two zone furnace: 200-1200 degC ( Min. Gauge Length: 120 mm)
Three zone furnace: 200-1200 degC (Min. Gauge length: 16 mm) **Threaded samples are required.
f) Three Point and Four Point bend fixtures
Minimum Span: 38 mm
Maximum Span: 305 mm
g) MTS High temperature grips for Threaded and Shouldered End Samples
4. Rotary Bending Fatigue System- 20Nm:
Specifications: Machine capacity: up to 20 Nm (Bending moment)
Operating speed: 200-10000 RPM
Speed resolution: 1 RPM
Operating temperature: ambient to 1000 degC
Temperature control: +/- 20 degC
Component diameter: 2-16 mm
Dead weight: 1N-3Nos., 2N-1No., 5N-1No., 10N-2Nos., 20N-1No., 50N-1No.
5. Digital Image Correlation (DIC):
The VIC-3D Fulcrum Module allows low-speed cameras to capture displacement and strain measurements during periodic, high-speed events. It allows users to accurately trigger low-speed cameras at peaks, valleys, or phase intervals in the driving frequency. Applications include fatigue tests.
Since VIC-3D calculates the Lagrangian strain tensor on the specimen surface, the transverse strain can be used to calculate the reduction in a cross-sectional area of the sample using a volume conservation constraint.
Technical specification related to high speed camera :
- Maximum image capture rate: 1,50,000 fps (at minimum resolution) and 2000 fps(at maximum resolution)
- Minimum image capture rate: 50 fps
- Maximum Resolution: 1280×1024 pixels
- Memory Capacity: 17,500 images at maximum resolution.
Working Principle :
1. Planar Biaxial System – 100kN:
It is a servo hydraulic machine which is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. It usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure that the output achieves the desired effect.It applies correctly only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed or other parameters. The system uses closed-loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism.
2. Axial Torsion Test System-250kN/2000Nm:
It is a servo hydraulic machine which is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. It usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure that output is achieving the desired effect.It applies correctly only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed or other parameters. The system uses closed-loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism.
3. Axial Fatigue System- 100kN:
It is a servo hydraulic machine which is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. It usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure that the output achieves the desired effect.It applies correctly only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed or other parameters. The system uses closed-loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism.
4. Rotary Bending Fatigue System- 20Nm:
The machine is designed based on the rotating beam principle. The load condition is similar to that of a simple beam symmetrically loaded at two points. When the load is applied, tensile and compressive stresses develop in the material below and above the neutral axis respectively. For the first one half revolutions, the stresses in the specimen originally below the neutral axis are reversed from tension to compression and vice versa. Upon completing the revolution, the stresses are again reversed so that during one revolution, the test specimen passes through a complete cycle of flexural stresses (tension and compression).
5. Digital Image Correlation (DIC):
DIC relies on finding the maximum of the correlation array between pixel intensity array subsets on two or more corresponding images, which gives the integer translational shift between them. The method tracks the changes in grey value pattern in small neighbourhoods called subsets during deformation.
Sample Preparation, User Instructions and Precautionary Measures
1. Planar Biaxial System – 100kN:
Sample Dimensions (mm): Preferable ASTM/equivalent standard samples
a) Gauge length: 200-350 mm
b) Width: 10-50 mm
c) Thickness: 0.5 - 19mm
2. Axial Torsion Test System-250kN/2000Nm:
Preferable ASTM/equivalent standard samples
a)Round
Gauge length: 20-300 mm
Diameter: 6-26 mm
b)Flat
Gauge length: 20-300 mm
Width: 10-50 mm
Thickness: ~0.5-25.9 mm
3. Axial Fatigue System- 100kN:
a) Round
Gauge length: 20-300 mm
Diameter: 6-22.9 mm
b) Flat
Gauge length: 20-300 mm
Width: 10-70 mm
Thickness: ~0.5-19 mm
4. Rotary Bending Fatigue System- 20Nm:
Preferable ASTM standard samples
a) At Room temperature
Gauge length: 60-200 mm
Diameter: 2-16 mm
b) At elevate temperature
Gauge length: 200 mm
Diameter: 2-16 mm
Charges for Analytical Services in Different Categories
TEST CHARGES AMTF LAB
Mechanical Testing (GST extra)
Test Name | IITB User (INR) | Non-IITB Academic (INR) | National R&D Lab. (INR) | Industries & Non Govt. Agencies (INR) |
Tensile Test | 200 * | 400 * | 800 * | 1600 * |
Compression | 200 * | 400 * | 800 * | 1600 * |
Torsion | 200 * | 600 * | 1200 * | 1600 * |
Axial Torsion | 400 * | 1200 * | 2400 * | 3200 * |
Biaxial Tension | 300 * | 900 * | 1800 * | 2400 * |
Three Point Bend | 400 * | 1200 * | 2400 * | 3200 * |
Four Point Bend | 400 * | 1200 * | 2400 * | 3200 * |
KIc (Pre-Crack + Testing) | (600 +300) * | (1800 +900)* | (3600 +1800)* | (4800 +2400)* |
JIc (Pre-Crack + Testing) | (600 +300) * | (1800 +900)* | (3600 +1800)* | (4800 +2400)* |
FCGR (Pre-crack+Testing) | (600 +300#) | (1800 +900#) | (3600 +1800#) | (4800 +2400#) |
Uniaxial Fatigue | 500 # | 1500 # | 3000 # | 4000 # |
Three/Four Point Bend Fatigue | 500 # | 1500 # | 3000 # | 4000 # |
Rotary Bending Fatigue | 500 # | 1500 # | 3000 # | 4000 # |
Torsion Fatigue | 500 # | 1500 # | 3000 # | 4000 # |
Tension-Torsion Fatigue | 600 # | 1800 # | 3600 # | 4800 # |
Biaxial Fatigue | 800 # | 2400 # | 4800 # | 6400 # |
Accessories (Rates as per the respective tests)
Accessories | IITB User (INR) | Non-IITB Academic (INR) | National R&D Lab. (INR) | Industries & Non Govt. Agencies (INR) |
Extensometer | 100 | 300 | 600 | 800 |
DIC | 300 | 900 | 1800 | 2400 |
Furnace | 500 | 1500 | 3000 | 4000 |
Clip On Gauge | 100 | 300 | 600 | 800 |
Cooling Chamber(Liq. N2 Charges Extra) | 800 | 2400 | 4800 | 6400 |
Video Extensometer | 200 | 600 | 1200 | 1600 |
* Per sample # Per hour
N.B : 1. GST-18% (as of now) for external users only.
2. Static test charges will be extra if it takes more than half an hour.
3. Any analysis (DIC or others) charges will be extra.
4. For other customised experiments will be quoted separately.
Applications
1.Planar Biaxial System – 100kN:
1.a) Aerospace and Power Generation: To study engine turbine materials, like metal alloys, ceramics and composites, to allow them to operate at increasingly higher temperatures for improved efficiency
1.b) Ground Vehicle: To validate new material models for sheet metal or composite components that are being used to meet more stringent fuel economy targets and increased safety requirements
1.c) Construction: To study advanced materials that are increasingly used to allow more complex designs, to address security issues from natural and man-made disasters and to meet environmental requirements.
1.d) Oil and Gas Pipeline Components: To evaluate the material properties for high temperature and corrosive environment. To design high efficiency turbine, pressure vessels, heat-exchanges etc.
1.e) Large Scale Wind Turbine Structures: Efficient design of wind turbine structures by evaluating the material properties at multiaxial loading.
2.Axial Torsion Test System-250kN/2000Nm: Axial-torsion testing machines help characterize biaxial mechanical properties of materials, both in static and dynamic conditions, which helps in choosing the right materials for different applications where components are exposed to axial torsion loading profiles.
2.a) Fatigue Testing This system is ideal for the exacting demands of material fatigue testing. Highly stiff integrated actuator beams, patented hydraulic grips, high resolution force transducers and precision alignment fixtures combine to deliver tightly controlled and consistent through-zero specimen loading. Example: Constant Amplitude, Variable Amplitude, Low Cycle Fatigue (LCF) and High Cycle Fatigue (HCF)
2.b) Fracture Testing The system can be readily configured to perform linear elastic and elastic-plastic fracture toughness testing. The system load frame can be used for both pre-cracking and fracture testing and equipped with a selection of standard compliant grips and precision clip-on displacement gauges. Example: Fracture Toughness, Fatigue Crack Growth, Crack Propagation, JIc and KIc
2.c) Component Testing Highly configurable MTS Axial Torsional System feature the test space and performance flexibility required to perform both static and dynamic component testing. These systems can be equipped with fixtures for single and multiple specimens, as well as a full selection of extensometers that are versatile enough to measure displacement from a variety of locations on a specimen. Example: Strength and Mechanical Properties of Components and Assemblies
2.d) Monotonic Testing Multipurpose MTS Axial Torsion systems are equipped to meet a full spectrum of monotonic—or static-material testing requirements. These systems run industry-leading MTS Test Suite software, which combines powerful test definition capabilities with simplified runtime operation and the ability to analyse data report test results in a variety of standard and custom formats. Example: Tensile, Compression, Bend and Stress Relaxation
3. Axial Fatigue System- 100kN:
3.a)Fatigue Testing The MTS Landmark system is ideal for the exacting demands of material fatigue testing. Highly stiff integrated actuator beams, patented hydraulic grips, high resolution force transducers and precision alignment fixtures combine to deliver tightly controlled and consistent through-zero specimen loading. Example: Constant Amplitude, Variable Amplitude, Low Cycle Fatigue (LCF) and High Cycle Fatigue (HCF)
3.b) Fracture Testing The system can be readily configured to perform linear elastic and elastic-plastic fracture toughness testing. The system load frame can be used for both pre-cracking and fracture testing and is equipped with a selection of standard compliant grips and precision clip-on displacement gauges. Example: Fracture Toughness, Fatigue Crack Growth, Crack Propagation, JIc and KIc
3.c) Component Testing Highly configurable MTS Landmark systems feature the test space and performance flexibility required to perform both static and dynamic component testing. These systems can be equipped with fixtures for single and multiple specimens, as well as a full selection of extensometers that are versatile enough to measure displacement from a variety of locations on a specimen. Example: Strength and Mechanical Properties of Components and Assemblies
3.d) Monotonic Testing Multipurpose MTS Landmark systems are equipped to meet a full spectrum of monotonic—or static-material testing requirements. These systems run industry-leading MTS Test Suite software, which combines powerful test definition capabilities with simplified runtime operation and the ability to analyse data report test results in a variety of standard and custom formats. Example: Tensile, Compression, Bend and Stress Relaxation Digital Image Correlation (DIC): Strain Contour on the specimen, strain on individual points, average and maximum strains and various other geometric data can be obtained by using DIC technique. Using the High Speed Camera, crack propagation can be clearly studied. Can use DIC to analyse images of in situ tensile or compression test.
4. Rotary Bending Fatigue System- 20Nm: To test the fatigue strength of materials under bending stress. It can be used in a variety of industries, including Automotive, Medical, Rail transit, Energy and Materials research.
Sample Details
--
--
--
--
--
--
SOP, Lab Policies and Other Details
Publications
Journal Publications:
1. " Fracture toughness characteristics of thermo-mechanically rolled direct quenched and partitioned steels" Gaurav Kumar, Sumit Ghosh, Sakari Pallaspuro, Mahesh Somani, Jukka Kömi ,Sushil K. Mishra , Amol A. Gokhale Material Science and Engineering A, Volume 840 (2022)
2."The Role of Microstructure Inhomogeneity in Ti-6Al-4V Forging on Fracture Toughness Behaviour", Anish Ranjan, Jyoti Shankar Jha, Sushil K. Mishra, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance. (2022)
3. Hitarth Maharaja, Bimal Das, Amit Singh, Sushil Mishra, “Comparative assessment of strain-controlled fatigue performance of SS 316L at room and low temperatures”, International Journal of Fatigue (2023)
4. A. H. Siddiqui, J. P. Patil, S. Mishra, “Design of a Biaxial Cruciform Specimen with a High Degree of Plastic Deformation and Yield Locus Evolution”, Experimental Mechanics (2023)
5.Micromechanics-based understanding of the stability of film-like austenite in steels
G Kumar, TK Bhandakkar, SK Mishra, AA Gokhale - Materials Science and Technology,
Journal of “Materials Science and Technology” (2023)
6. Stress Intensity Range Dependent Slowing Down of Fatigue Crack Growth under Strain‐Induced Martensitic Transformation of Film‐Like Retained Austenite G Kumar, S Ghosh, S Pallaspuro, MC Somani, J Kömi… - steel research international (2024)
7. Effect of crystallographic orientation on the formation of α-case in Ti-6Al-4Vtitanium alloy
Jornal of “ metallurgical and Materials transactions” (2024)
Oral Presentation:
Gaurav Kumar , Jeet Patil , Sakari Pallaspuro , Sumit Ghosh , Mahesh Somani , Sushil K. Mishra , Amol A. Gokhale "Tensile and Fracture Toughness Behaviour of Thermo-mechanically Rolled Direct Quenched & Partitioned (TMR-DQP) Steels".
Presented in :ASIA STEEL 2021 (5th-9th December 2021)
Paper presentation:
1. "Structural integrity assessments of Ni-Cr-Mo-V Steel", Satyaprakash Mishra, Anish Ranjan, Sushil Mishra, 8th international Conference on Product Life cycle Modeling and Synthesis (PLMSS) -2021, Paper Accepted for publication.
2. Yield Locus Develepment and Microstructure charactarisation of AA2219 under planar Biaxial Loading, Presented at IDDRG 2023 Sweden and NUMIFORM 2023 poland by priya Tiwari
3. Yield locus evolution of SS 316L at high strain: experimental and numerical modeling Presented at NUMIFORM2023 poland by Rubal Dongarwar
4. Maharaja, H., Das, B., Singh, A., Mishra, S., Enhancement in fatigue resistance at low temperature strain-controlled fatigue of SS 316L: Assisted by martensitic transformation,FEMS EUROMAT 2023
Poster Presentation:
1. Rubal Dongarwar, Sushil Mishra, Rakesh Mote, Rajeev Kapoor, "Phase transformation in SS316L by low cycle cryo fatigue and it's reversion", NMD ATM 2022
2. Anantha Lakshmi Prasanna Tatavarty, Amit Singh, Sushil Mishra, SVS Narayana Murty, “Modeling the low cycle fatigue behaviour of AA2219 aluminium alloy”, NMD ATM 2022
3. Priya Tiwari, Amit Singh, SVS Narayan Murty, Sushil k. Mishra, “Mechanical and Microstructural Characterisation of AA2219”, NMD ATM 2022
4. Anish Ranjan, Amit Kumar Singh, Sushil Mishra, “Local Anisotropy in Strain Response of an α/β Titanium Alloy”, NMD ATM 2022
